Elastic and Armis integrate to deliver real-time IoT security insights
.png)
IoT and unmanaged devices are some of the toughest blind spots for security teams today, and attackers know it. That’s why we’re excited to team up with Armis — an expert in device discovery and risk assessment — to bring its real-time device data right into Elastic Security. By combining Armis’s rich telemetry with Elastic Security’s analytics, ES|QL querying, and Elastic AI Assistant, analysts get the full picture of their device landscape. This means faster detection, smarter investigations, and quicker responses all in one place, helping you close those critical gaps before they become a problem.
Getting started is incredibly simple with Elastic’s agentless architecture. Just enter your Armis API key through Kibana’s Management > Integrations interface, and you’ll have real-time device data flowing into Elastic within minutes with no agents to deploy or infrastructure to manage. For organizations that prefer traditional agent-based installations, that option remains available. But the agentless approach makes it easier than ever to start correlating Armis insights with your existing security data.
Ingest and analyze Armis IoT data with Elastic
Once connected, the Armis integration brings three rich data streams into Elastic:
Devices: All devices monitored by Armis
Alerts: Alerts associated with all devices
- Vulnerabilities: Vulnerabilities and possible mitigation steps detected across all devices
Note: The vulnerability data stream maps devices to their specific risks, giving analysts clear visibility into which assets need urgent attention and how to remediate them. This helps you prioritize your efforts effectively, closing critical gaps before attackers can exploit them.
Out of the box, the integration includes three purpose-built Kibana dashboards that give SOC analysts clear, actionable views into devices, alerts, and vulnerabilities that help you quickly prioritize and respond to risks.
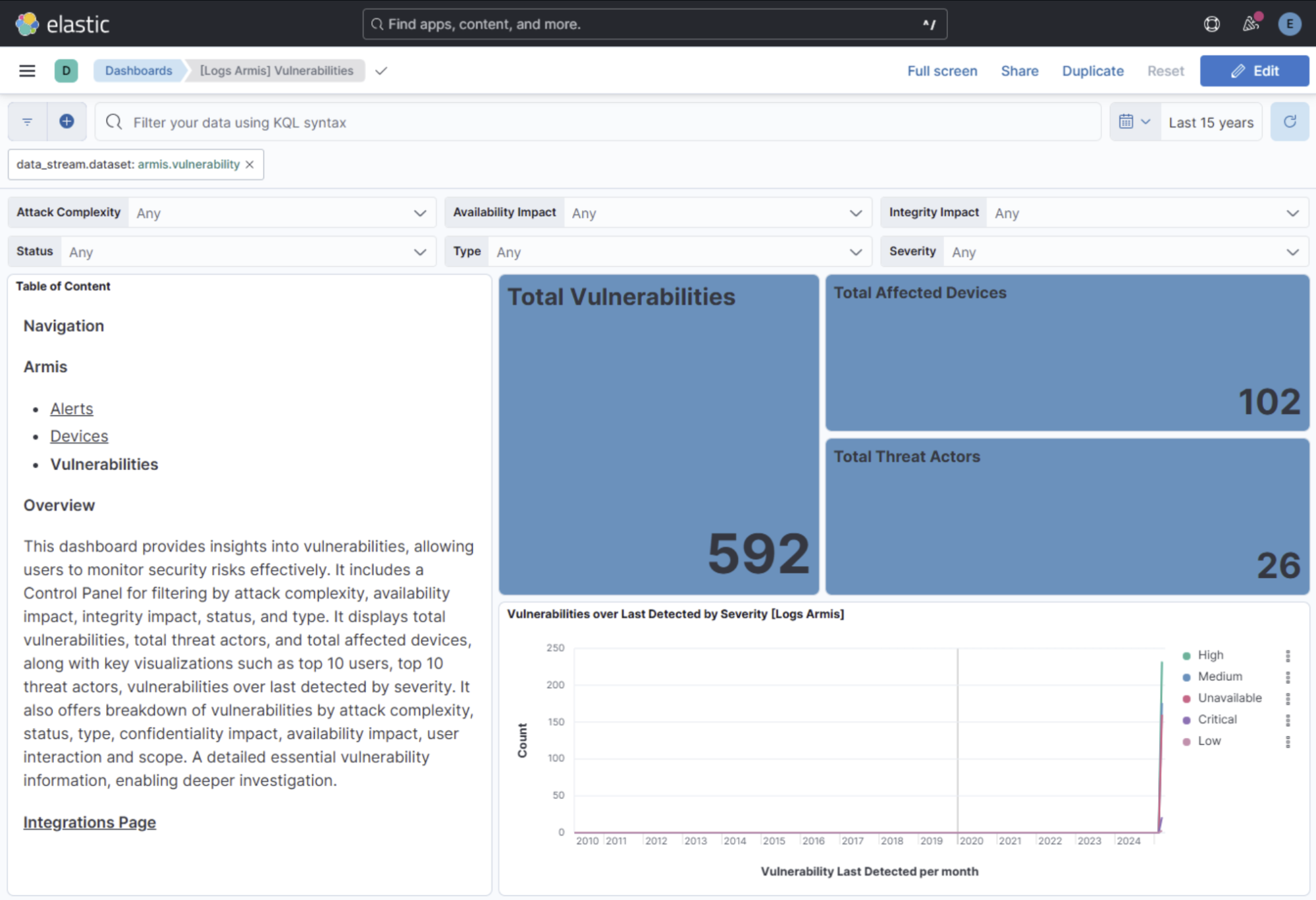
The Vulnerabilities dashboard provides essential threat intelligence, including CVSS scores, exploit availability, and affected device counts.
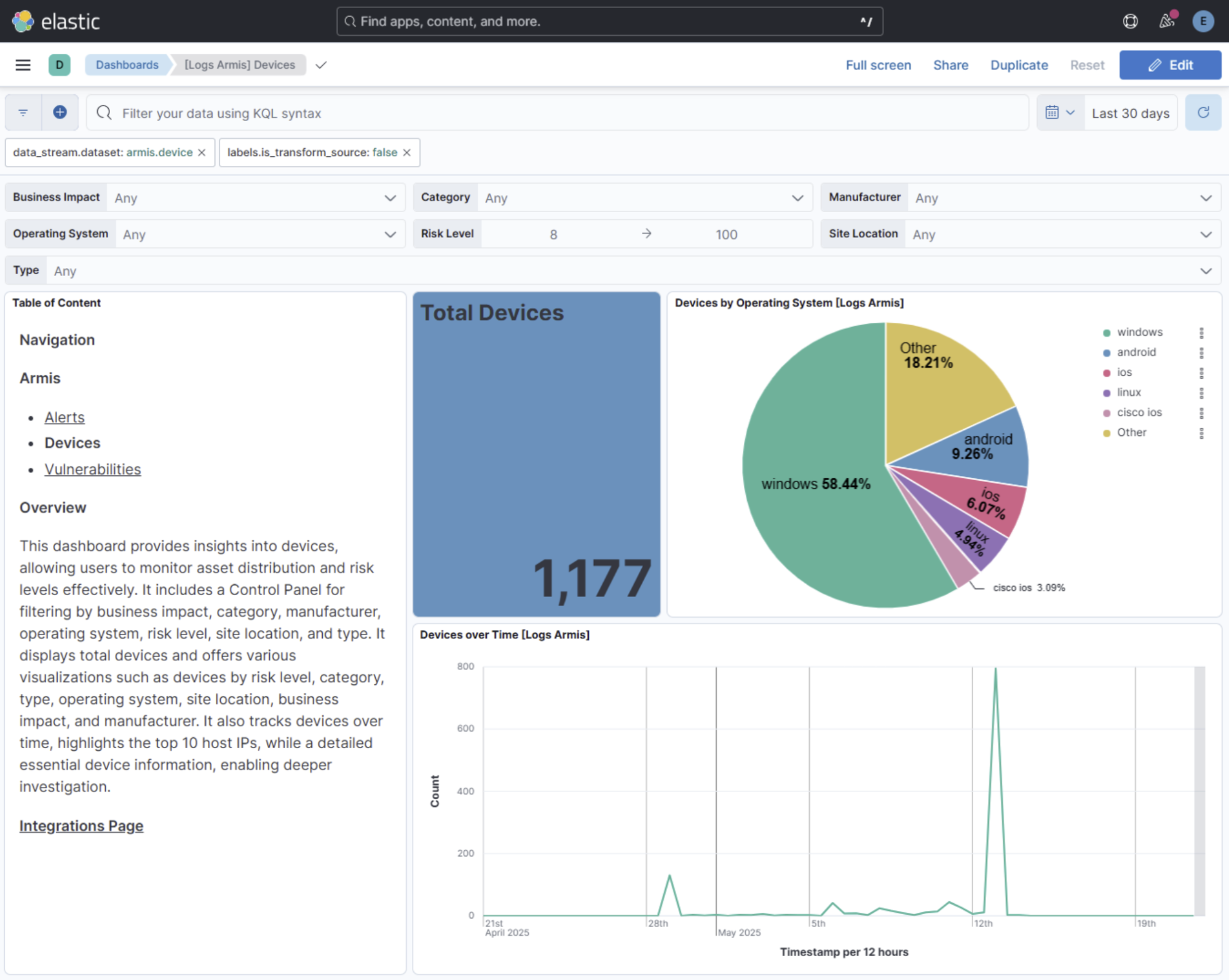
The Devices dashboard offers comprehensive asset visibility with risk scoring, business impact assessment, and geographic distribution.
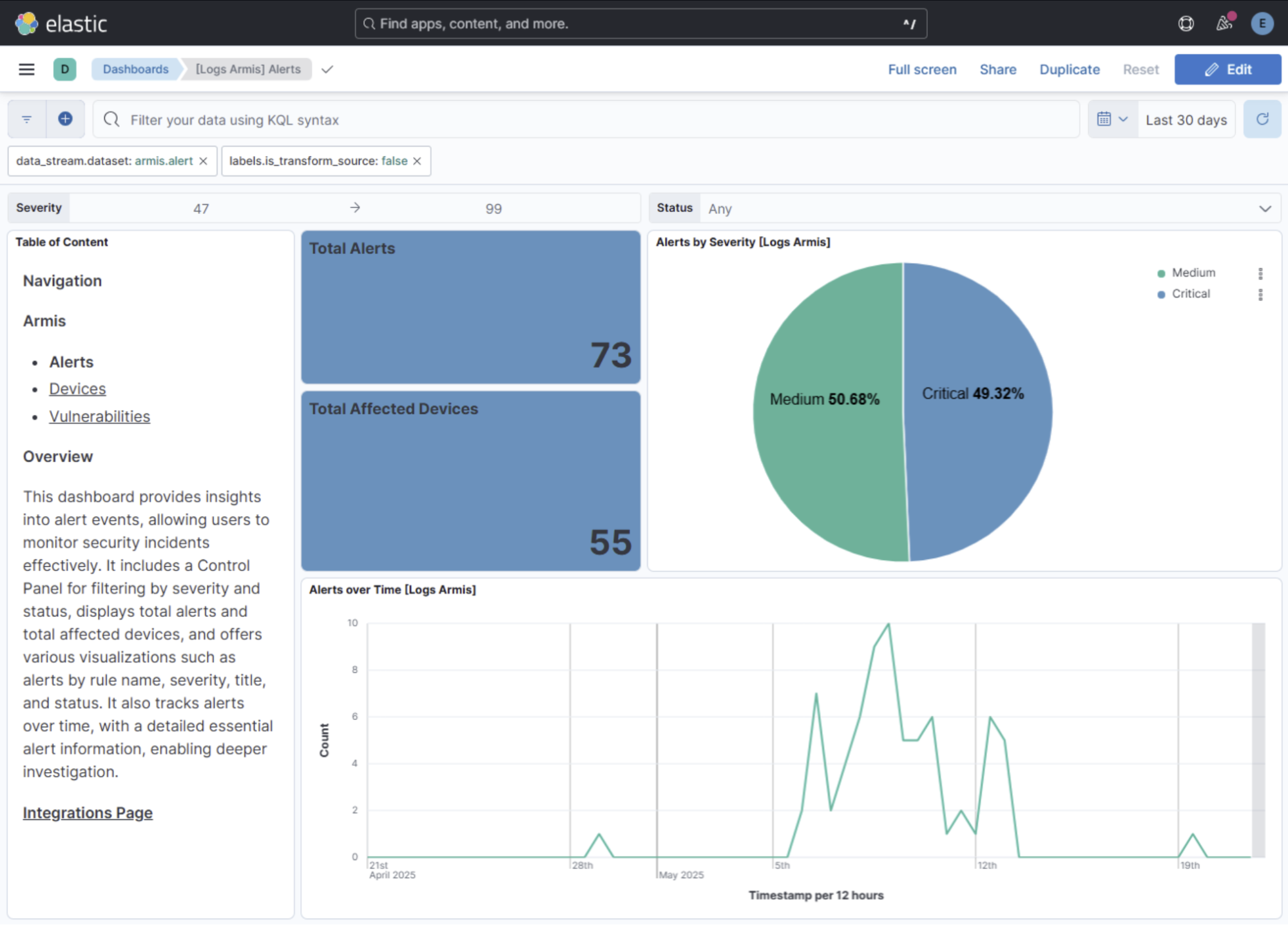
The Alerts dashboard enables rapid incident triage with severity filtering and timeline analysis.
Beyond basic data collection and overview dashboards, the real value of integrating Armis data into Elastic is that by normalizing Armis events to Elastic Common Schema (ECS), you can seamlessly correlate device telemetry with other security data sources like endpoint, network, and identity logs. This enables consistent field names, unified queries, and streamlined detection logic across your environment, making threat hunting and investigation faster and more reliable.
ES|QL is Elastic’s piped query language, which enables complex in-line correlation and enrichment; you no longer need to create enrichment policies to correlate across data streams and find context quickly. But during an active investigation, you likely don’t have time to read documentation to learn new query syntax. You can take ES|QL a step further by crafting powerful queries from natural language using Elastic AI Assistant.
From alert to investigation with ES|QL and Elastic AI Assistant
Imagine that you receive the Armis alert below about device ID “854” showing suspicious activity, and you want to quickly investigate if there are known exploits targeting that device type.
{
"@timestamp": "2025-03-29T00:12:57.306Z",
"agent": {
"ephemeral_id": "b8961f6d-527f-4e75-a54e-4440c07d7ff7",
"id": "6e0e7fed-f6da-48e7-aa1c-3ae3eb605196",
"name": "elastic-agent-41603",
"type": "filebeat",
"version": "8.18.0"
},
"armis": {
"alert": {
"activity_uuids": [
"6f3d6d3a-6732-44cc-9d63-10a38277fb15"
],
"affected_devices_count": 1,
"alert_id": "61",
"classification": "Security - Other",
"description": "The Armis security platform has detected a violation of a policy and generated an alert.",
"device_ids": [
"854"
],
"severity": "Critical",
"status": "Unhandled",
"status_change_time": "2025-03-29T00:12:57.306Z",
"time": "2025-03-29T00:12:57.306Z",
"title": "[Risk] Device Susceptible to Ransomware",
"type": "System Policy Violation"
}
},
"data_stream": {
"dataset": "armis.alert",
"namespace": "53950",
"type": "logs"
},
"ecs": {
"version": "8.17.0"
},
"elastic_agent": {
"id": "6e0e7fed-f6da-48e7-aa1c-3ae3eb605196",
"snapshot": false,
"version": "8.18.0"
},
"event": {
"agent_id_status": "verified",
"dataset": "armis.alert",
"id": "61",
"ingested": "2025-05-23T09:34:03Z",
"kind": "alert",
"original": "{\"activityUUIDs\":[\"6f3d6d3a-6732-44cc-9d63-10a38277fb15\"],\"affectedDevicesCount\":1,\"alertId\":61,\"classification\":\"Security - Other\",\"connectionIds\":[],\"description\":\"The Armis security platform has detected a violation of a policy and generated an alert.\",\"destinationEndpoints\":[],\"deviceIds\":[854],\"lastAlertUpdateTime\":null,\"mitreAttackLabels\":null,\"policyId\":null,\"policyLabels\":null,\"policyTitle\":null,\"severity\":\"Critical\",\"sourceEndpoints\":[],\"status\":\"Unhandled\",\"statusChangeTime\":\"2025-03-29T00:12:57.306928+00:00\",\"time\":\"2025-03-29T00:12:57.306928+00:00\",\"title\":\"[Risk] Device Susceptible to Ransomware\",\"type\":\"System Policy Violation\"}",
"severity": 99
},
"host": {
"id": [
"854"
]
},
"input": {
"type": "cel"
},
"message": "The Armis security platform has detected a violation of a policy and generated an alert.",
"observer": {
"product": "Asset Management and Security",
"vendor": "Armis"
},
"related": {
"hosts": [
"854"
]
},
"tags": [
"preserve_original_event",
"preserve_duplicate_custom_fields",
"forwarded",
"armis-alert"
]
}Open Elastic AI Assistant and prompt it to assist with the investigation:
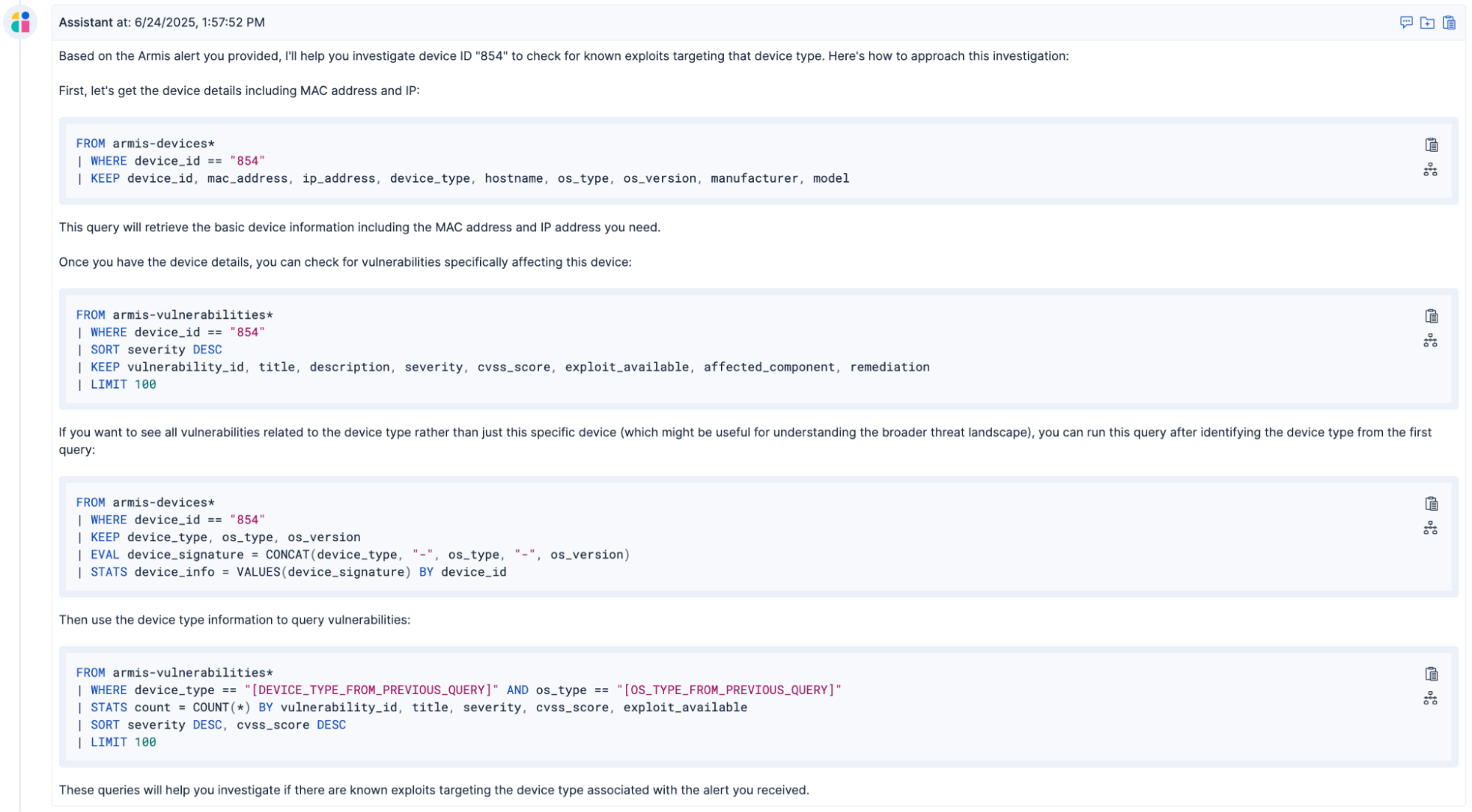
Elastic AI Assistant provides several ES|QL queries to break down the investigation into logical steps. It creates a complex investigation flow from natural language prompts — starting with device identification, expanding to vulnerability correlation, then broadening to device type analysis. Each query builds context for deeper investigation, and you can refine the queries based on what you discover.
First, gather device details:
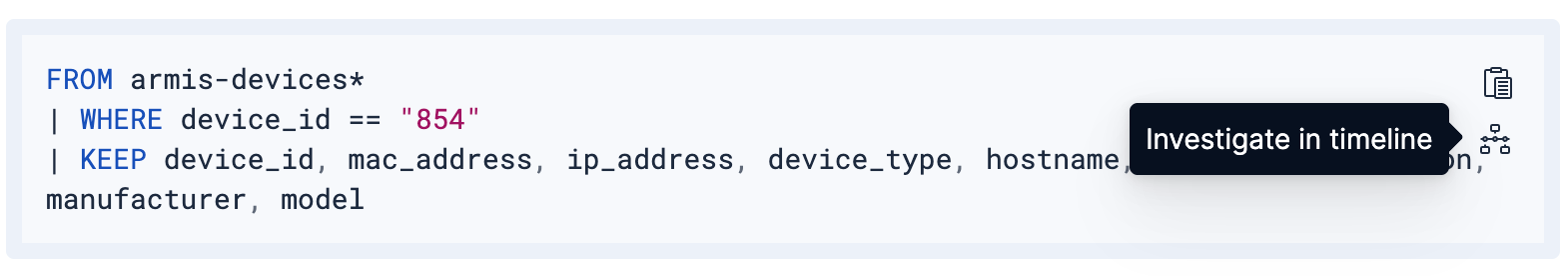
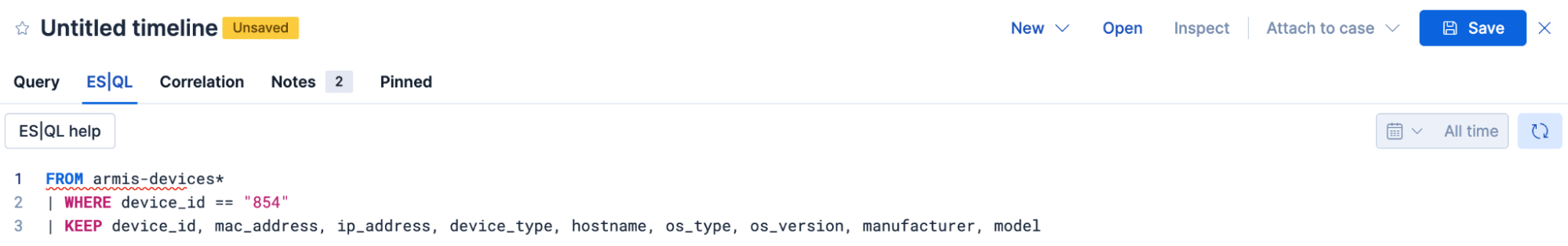
FROM armis-devices* | WHERE device_id == "854" | KEEP device_id, mac_address, ip_address, device_type, hostname, os_type, os_version, manufacturer, modelThen, check for device-specific vulnerabilities:
FROM armis-vulnerabilities* | WHERE device_id == "854" | SORT severity DESC | KEEP vulnerability_id, title, description, severity, cvss_score, exploit_available, affected_component, remediation | LIMIT 100Next, create a device signature:
FROM armis-devices* | WHERE device_id == "854" | KEEP device_type, os_type, os_version | EVAL device_signature = CONCAT(device_type, "-", os_type, "-", os_version) | STATS device_info = VALUES(device_signature) BY device_idFinally, expand to similar device types:
FROM armis-vulnerabilities* | WHERE device_type == "[DEVICE_TYPE_FROM_PREVIOUS_QUERY]" AND os_type == "[OS_TYPE_FROM_PREVIOUS_QUERY]" | STATS count = COUNT(*) BY vulnerability_id, title, severity, cvss_score, exploit_available | SORT severity DESC, cvss_score DESC | LIMIT 100The investigation starts by querying a single device, and then it expands to analyze the vulnerability profile for similar devices by:
Fetching specific device details from the armis-devices index for device “854” and retrieving identifiers like MAC address, IP address, device type, and operating system
Querying the armis-vulnerabilities index to find all known vulnerabilities affecting this particular device, sorted by severity to view critical threats first
Extracting the device signature (device type, OS type, and OS version) to create a broader threat profile beyond just this single device
Searching for all vulnerabilities affecting the same device signature, aggregated by vulnerability details and sorted by severity and CVSS score to understand the broader threat landscape for similar devices
You can kick off the investigation from within Elastic AI Assistant by clicking Investigate in timeline and be brought to Investigations > Timelines with the query prepopulated.
The benefit of using Elastic AI Assistant is that it’s smart about Elastic-specific syntax and can help you navigate field mappings and query optimization. For example, when running your own queries you may need to adjust field names to match Armis’ actual data structure. While this example focuses exclusively on Armis, the correlation possibilities expand across Elastic's 300+ integrations,- including endpoint data, threat intelligence feeds, network logs, and data from other leading security vendors.
Armis and Elastic for holistic, observable security
With this new integration, you can make Armis data a key part of your Elastic deployment for complete visibility into IoT devices while enabling cross-platform threat hunting and incident response.
If you’re not already using Armis for device security, explore its Armis Centrix™ platform for comprehensive IT, OT, IoT, and IoMT device visibility. If you’re already using Elastic for SIEM, add the Armis integration through Kibana’s Management > Integrations interface.
The release and timing of any features or functionality described in this post remain at Elastic's sole discretion. Any features or functionality not currently available may not be delivered on time or at all.
In this blog post, we may have used or referred to third party generative AI tools, which are owned and operated by their respective owners. Elastic does not have any control over the third party tools and we have no responsibility or liability for their content, operation or use, nor for any loss or damage that may arise from your use of such tools. Please exercise caution when using AI tools with personal, sensitive or confidential information. Any data you submit may be used for AI training or other purposes. There is no guarantee that information you provide will be kept secure or confidential. You should familiarize yourself with the privacy practices and terms of use of any generative AI tools prior to use.
Elastic, Elasticsearch, and associated marks are trademarks, logos, or registered trademarks of Elasticsearch N.V. in the United States and other countries. All other company and product names are trademarks, logos or registered trademarks of their respective owners.