In this article, we will discuss how to parse JSON fields in Elasticsearch, which is a common requirement when dealing with log data or other structured data formats. We will cover the following topics:
- Ingesting JSON data into Elasticsearch
- Using an Ingest Pipeline to parse JSON fields
- Querying and aggregating JSON fields
1. Ingesting JSON data into Elasticsearch
When ingesting JSON data into Elasticsearch, it is essential to ensure that the data is properly formatted and structured. Elasticsearch can automatically detect and map JSON fields, but it is recommended to define an explicit mapping for better control over the indexing process.
To create an index with a custom mapping, you can use the following API call:
PUT /my_index
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"message": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"json_field": {
"properties": {
"field1": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"field2": {
"type": "integer"
}
}
}
}
}
}In this example, we create an index called my_index with a custom mapping for a JSON field named json_field.
2. Using an Ingest Pipeline to parse JSON fields
If your JSON data is stored as a string within a field, you can use the Ingest Pipeline feature in Elasticsearch to parse the JSON string and extract the relevant fields. The Ingest Pipeline provides a set of built-in processors, including the json processor, which can be used to parse JSON data.
To create an ingest pipeline with the json processor, use the following API call:
PUT _ingest/pipeline/json_parser
{
"description": "Parse JSON field",
"processors": [
{
"json": {
"field": "message",
"target_field": "json_field"
}
}
]
}In this example, we create an ingest pipeline called json_parser that parses the JSON string stored in the message field and stores the resulting JSON object in a new field called json_field.
To index a document using this pipeline, use the following API call:
POST /my_index/_doc?pipeline=json_parser
{
"message": "{\"field1\": \"value1\", \"field2\": 42}"
}The document will be indexed with the parsed JSON fields:
{
"_index": "my_index",
"_type": "_doc",
"_id": "1",
"_source": {
"message": "{\"field1\": \"value1\", \"field2\": 42}",
"json_field": {
"field1": "value1",
"field2": 42
}
}
}3. Querying and aggregating JSON fields
Once the JSON fields are indexed, you can query and aggregate them using the Elasticsearch Query DSL. For example, to search for documents with a specific value in the field1 subfield, you can use the following query:
POST /my_index/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"json_field.field1": "value1"
}
}
}To aggregate the values of the field2 subfield, you can use the following aggregation:
POST /my_index/_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"field2_sum": {
"sum": {
"field": "json_field.field2"
}
}
}Conclusion
In conclusion, parsing JSON fields in Elasticsearch can be achieved using custom mappings, the Ingest Pipeline feature, and the Elasticsearch Query DSL. By following these steps, you can efficiently index, query, and aggregate JSON data in your Elasticsearch cluster.
Ready to try this out on your own? Start a free trial.
Want to get Elastic certified? Find out when the next Elasticsearch Engineer training is running!
Related content
September 11, 2025
Using LangExtract and Elasticsearch
Learn how to extract structured data from free-form text using LangExtract and store it as fields in Elasticsearch.
September 18, 2025
Elasticsearch open inference API adds support for Google’s Gemini models
Learn how to use the Elasticsearch open inference API with Google’s Gemini models for content generation, question answering, and summarization.

Introducing the ES|QL query builder for the Python Elasticsearch Client
Learn how to use the ES|QL query builder, a new Python Elasticsearch client feature that makes it easier to construct ES|QL queries using a familiar Python syntax.

September 4, 2025
Transforming data interaction: Deploying Elastic’s MCP server on Amazon Bedrock AgentCore Runtime for crafting agentic AI applications
Transform complex database queries into simple conversations by deploying Elastic's search capabilities on Amazon Bedrock AgentCore Runtime platform.
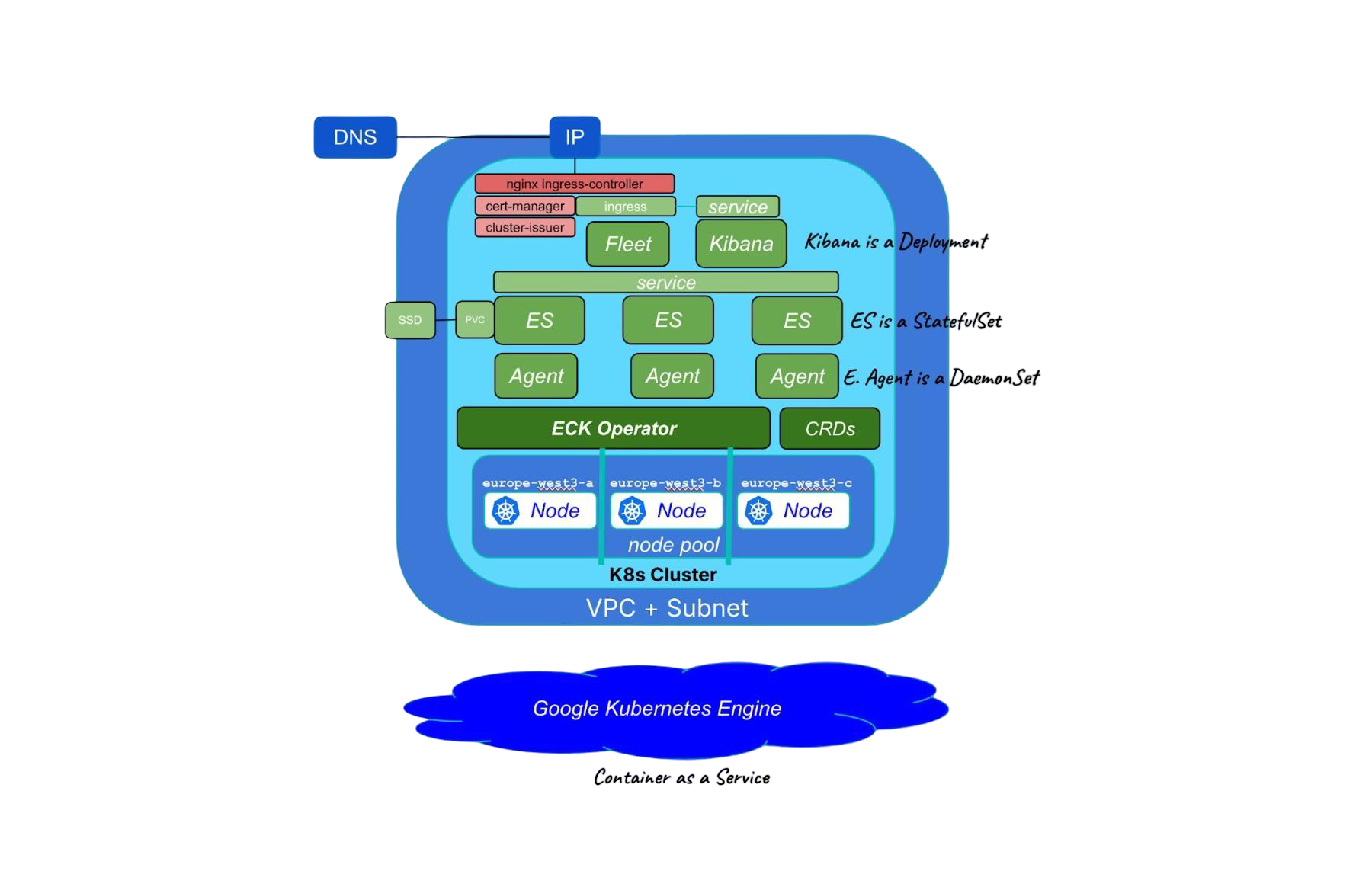
September 5, 2025
Running cloud-native Elasticsearch with ECK
Learn how to provision a GKE cluster with Terraform and run the Elastic Stack on Kubernetes using ECK.