Searching for documents containing specific substrings within a field is a common requirement in Elasticsearch. In this article, we will explore advanced techniques for querying Elasticsearch to find documents where a field contains a specific substring. We will discuss the use of query_string, match_phrase, and wildcard queries, the use of analyzers and tokenizers to improve search accuracy, and the available ES|QL functions to locate substrings in fields. If you want to learn about the usage of exact values vs. full text, check out this guide.
1. Query string query
The query_string query is a powerful and flexible way to search for documents containing a specific substring. It allows you to use the Lucene query syntax, which provides a wide range of search options. Here’s an example of a query_string query that searches for documents containing the substring “example”:
GET /_search
{
"query": {
"query_string": {
"query": "*example*"
}
}
}In this example, the asterisks (*) are used as wildcard characters, which match any sequence of characters. The query_string query will return documents containing the substring “example” in any field. Beware, though, as leading wildcards can be detrimental to your cluster performance.
2. Match phrase query
The match_phrase query is another option for searching for documents containing a specific substring. It searches for the exact phrase within a field, and it can be used with the slop parameter to allow for variations in word order. Here’s an example of a match_phrase query that searches for documents containing the substring “quick brown”:
GET /_search
{
"query": {
"match_phrase": {
"field_name": "quick brown"
}
}
}In this example, the match_phrase query will return documents containing the exact phrase “quick brown” in the specified field.
3. Wildcard query
The wildcard query is a simple way to search for documents containing a specific substring. It uses wildcard characters to match any sequence of characters within a field. Here’s an example of a wildcard query that searches for documents containing the substring “exam”:
GET /_search
{
"query": {
"wildcard": {
"field_name": "*exam*"
}
}
}In this example, the wildcard query will return documents containing the substring “exam” in the specified field. In this case, you also need to pay special attention when using leading wildcards in a wildcard query as this can slow down your search performance.
4. Analyzers and tokenizers
To improve the accuracy of substring searches, you can use analyzers and tokenizers to process the text in your documents. Analyzers are responsible for breaking down text into tokens, which are then used for indexing and searching. Tokenizers are a component of analyzers that split text into individual tokens.
For example, you can use the n-gram tokenizer to create tokens of varying lengths from the input text. This can help improve the accuracy of substring searches by allowing Elasticsearch to match substrings of different lengths. Here’s an example of how to create a custom analyzer with an n-gram tokenizer:
PUT /my_index
{
"settings": {
"analysis": {
"analyzer": {
"my_analyzer": {
"tokenizer": "my_tokenizer"
}
},
"tokenizer": {
"my_tokenizer": {
"type": "ngram",
"min_gram": 3,
"max_gram": 5
}
}
}
}
}In this example, the custom analyzer uses an n-gram tokenizer with a minimum token length of 3 and a maximum token length of 5. You can then use this custom analyzer when indexing your documents and when performing substring searches.
It should be noted that tokenizing very large bodies of text into n‑grams can significantly increase the number of terms in your inverted index, which in turn can unnecessarily increase storage and slow both indexing and querying. It is best to apply an n‑gram tokenizer to text fields where substring matching is essential.
5. ES|QL functions
LOCATE
The ES|QL LOCATE function will find the first occurrence of a given substring within a document. The LOCATE function is called thusly:

Here, the string is the field to query, substring is the target substring, and start is the integer offset within the string. This returns the integer position of the first occurrence of the substring occurring after the provided start integer position or a 0 if the substring does not exist.
For multiple occurrences of a substring in a field, this function may not be advisable, as there is no iterative processing in ES|QL and it is a purely declarative, pipeline-style query language.
MATCH
The MATCH function will return a boolean true if a substring passed into the query parameter is found within the text that is passed into the field parameter. It is suitable for general full-text search where relevance is determined by the presence of the terms, regardless of their position.

Optional functional named parameters may be passed in for finer granularity, such as fuzziness, operators to interpret text, and leniency values.
Note that the query may contain multiple terms and the results may include any of the terms, but not necessarily in the given order.
Example: Searching for "quick brown fox" would match documents containing "the fox is quick and brown".
MATCH_PHRASE
MATCH_PHRASE is similar to the MATCH function, yet it will necessarily match the entire phrase of terms provided to the function rather than match the individual terms. It is useful when you want to search for an exact phrase rather than just the presence of individual terms.

MATCH_PHRASE also has optional named functions that allow various refinements, such as slop and a token analyzer.
Example: Searching for "quick brown fox" would only match documents containing the exact phrase "quick brown fox".
KQL
A KQL query refers to a query written in the Kibana Query Language (KQL). KQL is a search and filter language used in Kibana, our Data visualization tool. Elastic has brought this query language into ES|QL for enhanced searches.
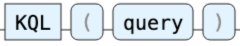
Example: Searching for “foo: bar” AND “baz > 12” would return all documents where the “foo” field contains “bar” and necessarily the “baz” field value is greater than 12.
QSTR
QSTR is a query format used by Lucene, which provides flexible, relevance-based searches on text fields, similar to how one would use a match query in the Elasticsearch DSL.
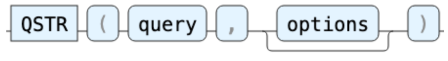
Example: Searching "timeout error OR \"connection refused\"" with QSTR in a ticketing index returns for ticket documents containing either "timeout error" or the exact phrase "connection refused."
QSTR also has the most options to choose from, offering high granularity and flexibility in your search.
Bonus: Interval queries and span
Interval queries
Interval Queries are queries that search for terms that necessarily follow a given sequence of occurrences. Here is a sample query:
POST _search
{
"query": {
"intervals" : {
"my_text" : {
"all_of" : {
"ordered" : true,
"intervals" : [
{
"match" : {
"query" : "it's rainy outside",
"max_gaps" : 0,
"ordered" : true
}
},
{
"any_of" : {
"intervals" : [
{ "match" : { "query" : "curl up with a good book" } },
{ "match" : { "query" : "listen to a podcast" } }
]
}
}
]
}
}
}
}
}This searches for the term “it’s rainy outside” followed by either the term “curl up with a good book” or “listen to a podcast.”
This sentence would create a match: “When it’s rainy outside, I like to dress up in cozy clothes, turn on some classical music, and curl up with a good book.”
This sentence would NOT create a match: “I find it best to listen to a podcast in my car when there’s a lot of traffic and it’s rainy outside.”
This is due to the “all_of”: {“ordered”: true} clause, which requires the ordering sequence as defined above.
This is an extremely powerful and extensible query that should be considered for dynamic and complex substrings.
Span
Span queries offer a low-level, position-aware method for substring search by operating on token offsets instead of raw text. Spans can nest child spans that must satisfy constraints such as appearing before or after another span within a specified distance. This makes them ideal for domains (like legal documents) where common terms acquire distinct meaning when they occur near certain keywords.
GET /_search
{
"query": {
"span_near": {
"clauses": [
{ "span_term": { "field": "contract" } },
{ "span_term": { "field": "breach" } }
],
"slop": 3,
"in_order": false
}
}
}For example, you might use a span_near query to find “contract” within four tokens of “breach.” A lengthy legal brief could mention “contract” dozens of times, but only include the phrases “breach of obligation and contract” or “breach of contract litigation” in two places. By tuning your span distance allowances (e.g. slop: 3), you’ll match only those two contexts and ignore all the other “contract” occurrences.
Conclusion
Elasticsearch provides several advanced techniques for querying documents containing specific substrings. By using query_string, match_phrase, and wildcard queries, custom analyzers and tokenizers, ES|QL functions, or even query intervals or spans, you can improve the accuracy and flexibility of your substring searches. Experiment with these techniques to find the best approach for your specific use case and dataset.
Ready to try this out on your own? Start a free trial.
Want to get Elastic certified? Find out when the next Elasticsearch Engineer training is running!
Related content

Introducing the ES|QL query builder for the Python Elasticsearch Client
Learn how to use the ES|QL query builder, a new Python Elasticsearch client feature that makes it easier to construct ES|QL queries using a familiar Python syntax.

September 4, 2025
Transforming data interaction: Deploying Elastic’s MCP server on Amazon Bedrock AgentCore Runtime for crafting agentic AI applications
Transform complex database queries into simple conversations by deploying Elastic's search capabilities on Amazon Bedrock AgentCore Runtime platform.
September 5, 2025
Running cloud-native Elasticsearch with ECK
Learn how to provision a GKE cluster with Terraform and run the Elastic Stack on Kubernetes using ECK.
September 1, 2025
Using UBI in Elasticsearch: Creating an app with UBI and search-ui
Learn how to use UBI in Elasticsearch through a practical example. We’ll be creating an application that produces UBI events on search and click results.

August 28, 2025
Using ES|QL COMPLETION + an LLM to write a Chuck Norris fact generator in 5 minutes
Discover how to use the ES|QL COMPLETION command to turn your Elasticsearch data into creative output using an LLM in just a few lines of code.