Update: April 16th, 2024
OpenAI has discontinued the use of plugins in ChatGPT. You can read more about this here. We recommend reading this tutorial instead to learn how to build a large language model (LLM) chatbot that uses a pattern known as Retrieval-Augmented Generation. You can also read this blog to learn how to create custom GPTs with Elastic data.
You may have read this previous blog post about our journey to connect Elasticsearch’s relevance capabilities with OpenAI question-answering capabilities. The key idea in that post was to illustrate how to use Elastic with OpenAI’s GPT model to build a response and return context-relevant content to users.
The application that we built can expose a search endpoint and be called by any front-end service. The good news is that now OpenAI has released a private alpha of the future ChatGPT plugin framework.
In this blog, you will learn how to implement the plugin and extend the use of ChatGPT to any content indexed in Elasticsearch, using the Elastic documentation.

What is a ChatGPT plugin?
ChatGPT plugins are extensions that are developed to assist the model in completing its knowledge or executing actions.
For example, we know that the cutover of ChatGPT from a knowledge perspective is September 2021, so any question on recent data won’t be answered. In addition, any question that relates to something too specific beyond the boundaries of what the model has been trained on won’t be answered.
Plugins can broaden the scope of possible applications and enhance the capabilities of the models, but reciprocally, the plugin's output is augmented by the model itself.
The official list of plugins currently supported by ChatGPT are listed below. You can expect this list to expand rapidly as more organizations experiment with ChatGPT:

As you scan through the list, you’ll notice that the use cases are slowly revealing themselves here. In the case of Expedia, for example, its plugin is extending ChatGPT to assist in planning travel, making ChatGPT a trip-planning assistant.
This blog aims to achieve similar objectives for Elastic — to allow ChatGPT to access Elastic’s current knowledge base and assist you with your Elastic projects.
Architecture
We are going to bring a slight modification that has a positive cost impact in the sample code presented in part 1 by my colleague Jeff Vestal.
We will remove the call to OpenAI API, as now ChatGPT will fulfill the role of taking the content from Elasticsearch and digesting it back to the user:
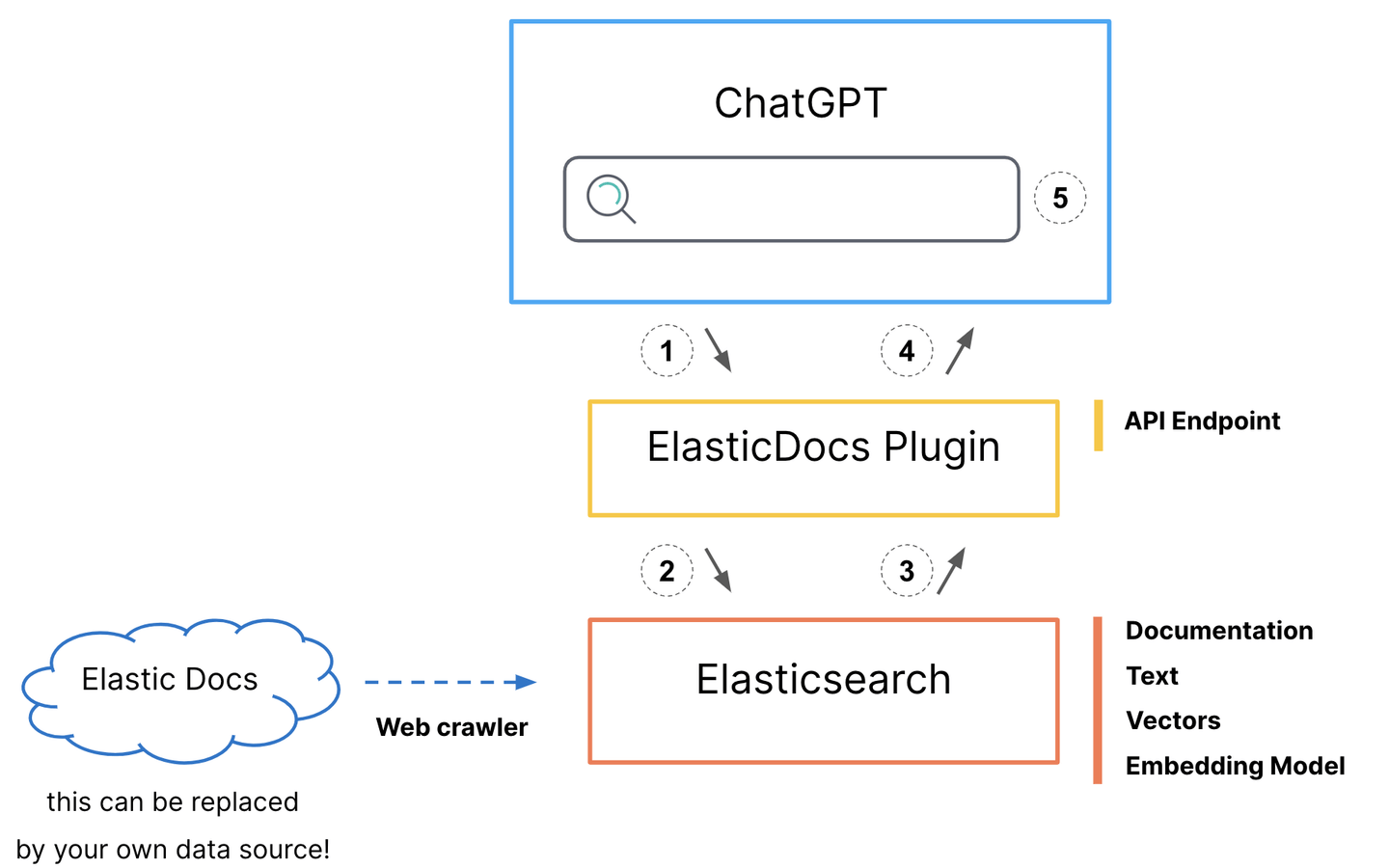
- ChatGPT makes a call to the
/searchendpoint of the plugin.
- This decision is based on the plugin “rules”
description_for_human(see plugin-manifest below).
- The plugin code creates a search request that is sent to Elasticsearch.
- Documentation body and original url are returned to Python.
- The plugin returns the document body and url, in text form to ChatGPT.
- ChatGPT uses the information from the plugin to craft its response.
Again, this blog post assumes that you have set up your Elastic Cloud account, vectorized your content, and have an Elasticsearch cluster filled with data ready to be used. If you haven’t set all that up, see our previous post for detailed steps to follow.
Plugin code
OpenAI built a fairly simple-to-handle plugin framework for ChatGPT. It deploys a service that exposes:
- The plugin manifest, explaining what the plugin provides to the users and to ChatGPT
- The plugin openAPI definition, which is the functional description that enables ChatGPT to understand the available APIs The plugin code can be found here.
Plugin file structure
The screenshot below shows what the structure looks like:
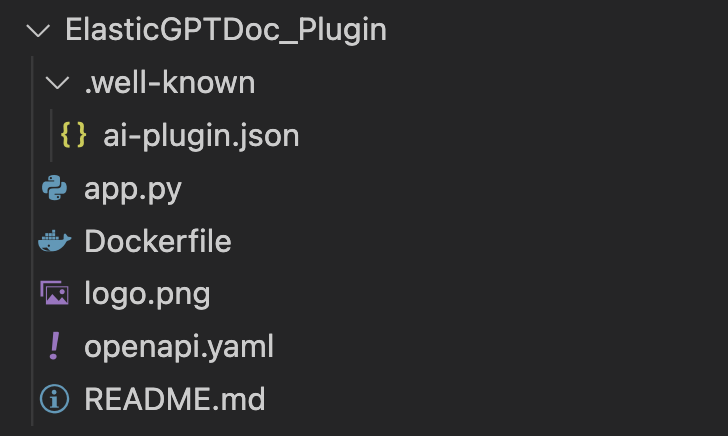
- The plugin manifest is stored in the ai-plugin.json file under the .well-known directory as per OpenAI best practices.
- The main service code is in app.py.
- The Dockerfile will be later used to deploy the plugin to Google Cloud Compute.
- The plugin’s logo (logo.ong) as displayed in the ChatGPT plugin store, here the Elastic logo.
- The OpenAI description of the plugin.
Python code
For the full code, refer to the GitHub repository. We are going to look only at the main part of this code:
…
@app.get("/search")
…
@app.get("/logo.png")
…
@app.get("/.well-known/ai-plugin.json")
…
@app.get("/openapi.yaml")
…We took out all the details and kept the main parts here. There are two categories of APIs here:
- The one required by OpenAI to build a plugin:
- /logo.png: retrieve the plugin logo
- /.well-known/ai-plugin.json: fetches the plugin manifest
- /openapi.yaml: fetches the plugin OpenAPI description
- The plugin API:
- /search is the only one here exposed to ChatGPT that runs the search in Elasticsearch
Plugin manifest
The plugin manifest is what ChatGPT will use to validate the existence (reachable) of the plugin. The definition is the below:
{
"schema_version": "v1",
"name_for_human": "ElasticGPTDoc_Plugin",
"name_for_model": "ElasticGPTDoc_Plugin",
"description_for_human": "Elastic Assistant, you know, for knowledge",
"description_for_model": "Get most recent elasticsearch docs post 2021 release, anything after release 7.15",
"auth": {
"type": "none"
},
"api": {
"type": "openapi",
"url": "PLUGIN_HOSTNAME/openapi.yaml",
"is_user_authenticated": false
},
"logo_url": "PLUGIN_HOSTNAME/logo.png",
"contact_email": "info@elastic.co",
"legal_info_url": "http://www.example.com/legal"
}There are a couple of things to point out here:
- There are two descriptions:
- description_for_human - This is what the human sees when installing the plugin in the ChatGPT web UI.
- description_for_model - Instructions for the model to understand when to use the plugin.
- There are some placeholders such as PLUGIN_HOSTNAME that are replaced in the Python code.
OpenAPI definition
Our code will only expose a single API endpoint to ChatGPT allowing it to search for Elastic documentation. Here is the description:
openapi: 3.0.1
info:
title: ElasticDocGPT
description: Retrieve information front the most recent Elastic documentation
version: 'v1'
servers:
- url: PLUGIN_HOSTNAME
paths:
/search:
get:
operationId: search
summary: retrieves the document matching the query
parameters:
- in: query
name: query
schema:
type: string
description: use to filter relevant part of the elasticsearch documentations
responses:
"200":
description: OKFor the definition file, the key points are:
- We take the ChatGPT prompt content and pass it as a query to our Elasticsearch cluster.
- Some placeholders such as PLUGIN_HOSTNAME are replaced in the Python code.
Deploying the Elastic plugin in Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
You have a choice in picking a deployment method to expose your plugin, as well as using a different cloud provider. We use GCP in this blog post — more specifically Google Cloud Run and Google Cloud Build. The first is to expose and run the service, and the second is for continuous integration.
Setup
This setup assumes your GCP user has the right permissions to:
- Build a container image with Google Cloud Build in the Google Container Registry
- Deploy a container in Google Cloud Run
If not, you will need to update permissions on the GCP IAM page.
We are going to use the gcloud CLI to set up our environment. You can find the installation instructions here.
Once installed, run the following command to authenticate:
gcloud authThen set the project identifier to your GCP project:
gcloud config set project PROJECT_IDYou are now ready to build and deploy.
Build and deploy
The first step is to build the container image using Cloud Build and push it to the Google Container Registry:
gcloud builds submit --tag gcr.io/PROJECT_ID/my-python-appReplace PROJECT_ID with your GCP project ID and my-python-app with the name you want to give to your container image.
Export the environment required by the Python code to create the Elasticsearch client:
export YOUR_CLOUD_ID=VALUE
export YOUR_CLOUD_PASS=VALUE
export YOUR_CLOUD_USER=VALUEFinally, deploy the container image to Cloud Run:
gcloud run deploy my-python-app \
--image gcr.io/PROJECT_ID/my-python-app \
--platform managed \
--region us-central1 \
--allow-unauthenticated \
--set-env-vars cloud_id=YOUR_CLOUD_ID,cloud_pass=YOUR_CLOUD_PASS,cloud_user=YOUR_CLOUD_USERYou should see your service running in Cloud Run:
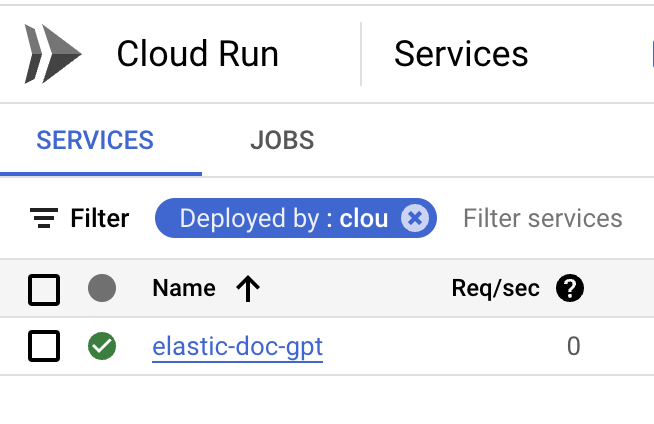
Note that you can also activate the continuous integration so that any commit in your GitHub repository will trigger a redeploy. On the service details page, click on Set up continuous deployment.

Installing the plugin in ChatGPT
Once the plugin is deployed and has a publicly accessible endpoint, it can be installed in ChatGPT. In our case, since this is deployed in Google Cloud Run, you can get the URL here:

Then in ChatGPT, go in the plugin store:
Choose to do “Develop your own plugin”:
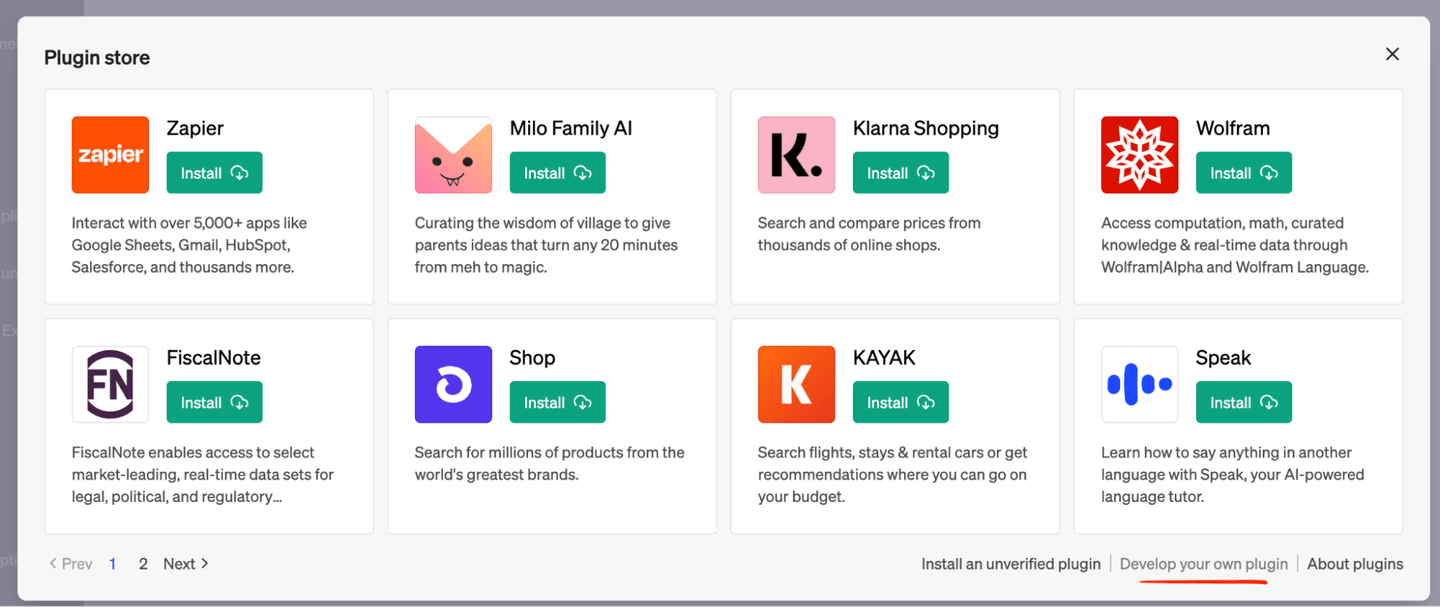
Paste the URL you copied from the Google Cloud Run page:
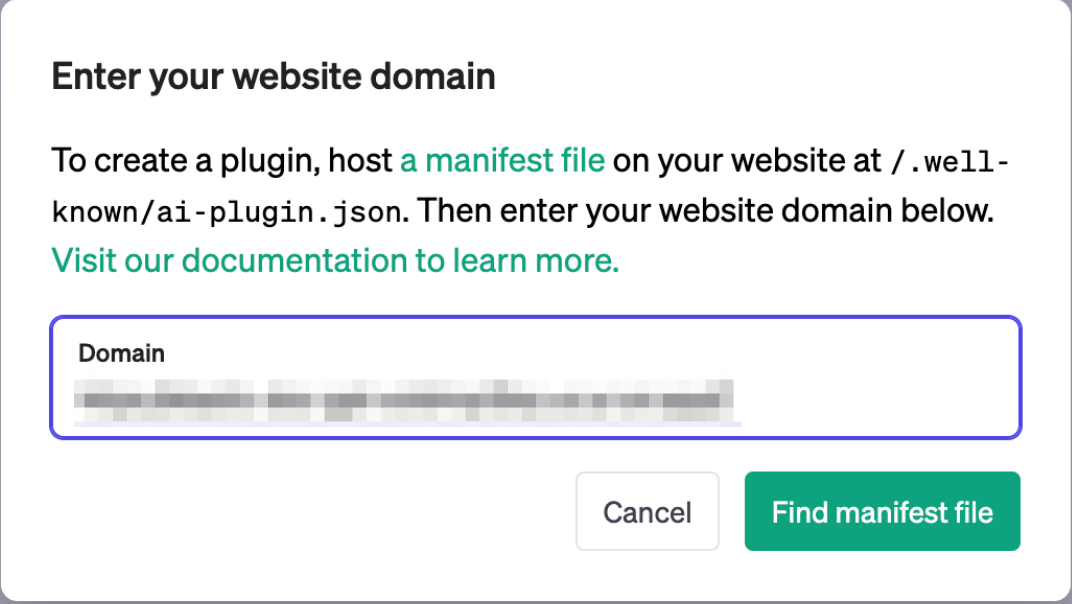
Ensure the plugin is found and valid:
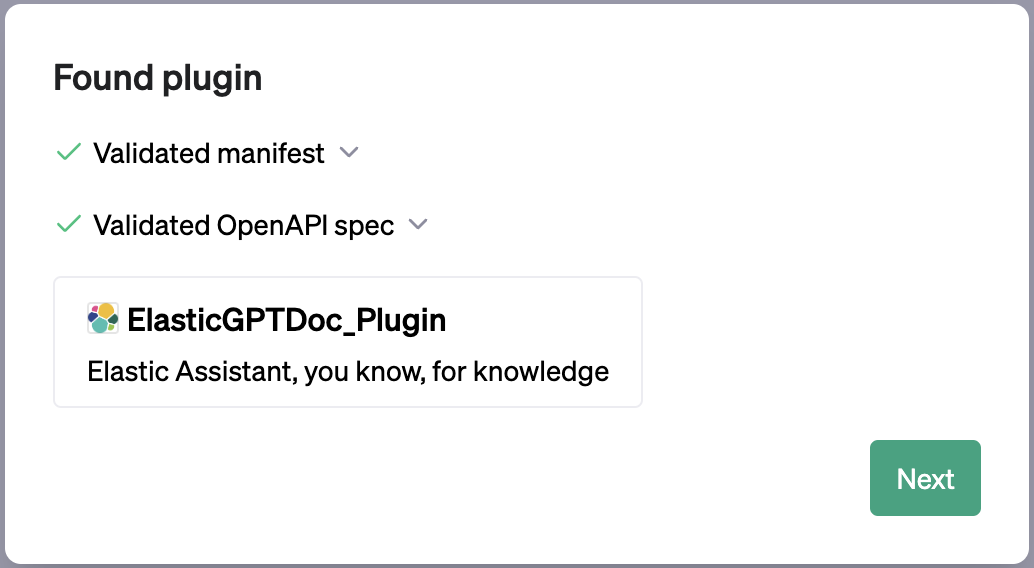
Follow the installation instructions until you see your plugin available in the list:
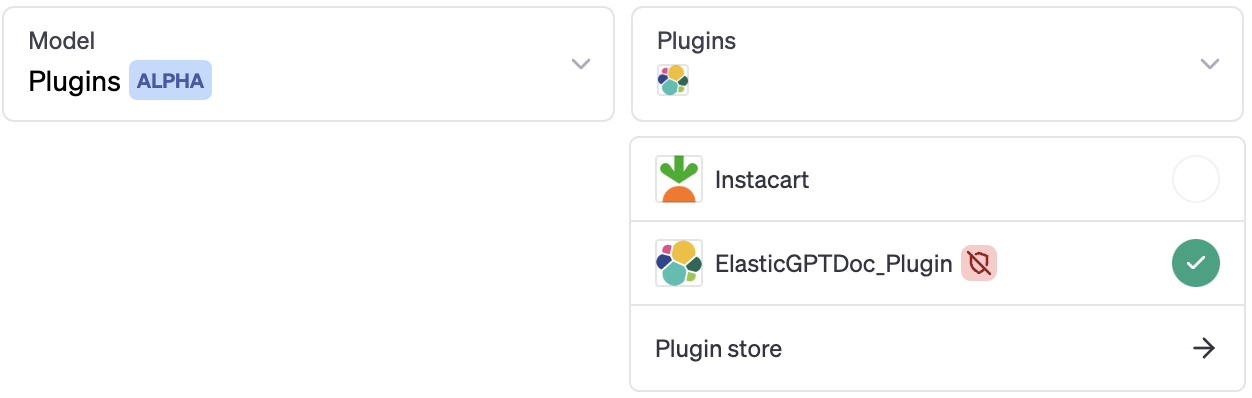
Let’s test our plugin!
OK, now for the best part! Do remember that ChatGPT decides to delegate when your prompt goes beyond its knowledge. To ensure that happens, just ask a question similar to this example:
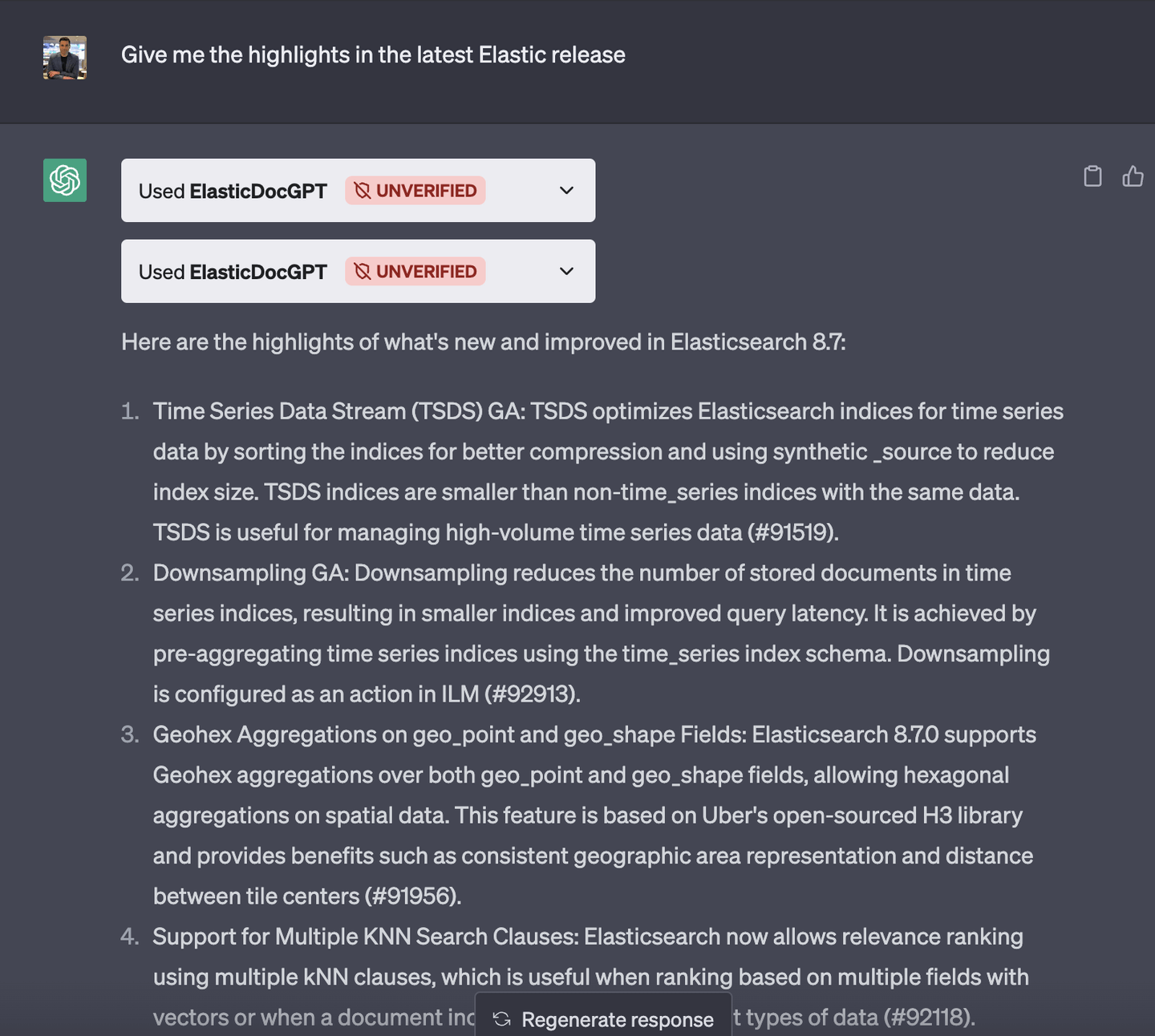
With the steps provided in this blog, you can create your own plugin and deploy it on a cloud provider or your own hosts. This allows you to start exploring enhancing ChatGPT's knowledge and functionality, enhancing an already amazing tool with specialized and proprietary knowledge.
You can try all of the capabilities discussed in this blog today! Get started by signing up for a free Elastic Cloud trial.
Here are some other blogs you may find interesting:
- ChatGPT and Elasticsearch: OpenAI meets private data
- Monitor OpenAI API and GPT models with OpenTelemetry and Elastic
- Exploring the Future of Security with ChatGPT
In this blog post, we may have used third party generative AI tools, which are owned and operated by their respective owners. Elastic does not have any control over the third party tools and we have no responsibility or liability for their content, operation or use, nor for any loss or damage that may arise from your use of such tools. Please exercise caution when using AI tools with personal, sensitive or confidential information. Any data you submit may be used for AI training or other purposes. There is no guarantee that information you provide will be kept secure or confidential. You should familiarize yourself with the privacy practices and terms of use of any generative AI tools prior to use.
Elastic, Elasticsearch and associated marks are trademarks, logos or registered trademarks of Elasticsearch N.V. in the United States and other countries. All other company and product names are trademarks, logos or registered trademarks of their respective owners.
Ready to try this out on your own? Start a free trial.
Elasticsearch has integrations for tools from LangChain, Cohere and more. Join our Beyond RAG Basics webinar to build your next GenAI app!
Related content

September 8, 2025
MCP for intelligent search
Building an intelligent search system by integrating Elastic's intelligent query layer with MCP to enhance the generative efficacy of LLMs.

September 4, 2025
What is Context Engineering?
Have you heard of this new term context engineering, but aren't sure what it is? Join us as we explain what it is and how RAG with Elasticsearch can help.

August 28, 2025
Using ES|QL COMPLETION + an LLM to write a Chuck Norris fact generator in 5 minutes
Discover how to use the ES|QL COMPLETION command to turn your Elasticsearch data into creative output using an LLM in just a few lines of code.

July 30, 2025
Building intelligent duplicate detection with Elasticsearch and AI
Explore how organizations can leverage Elasticsearch to detect and handle duplicates in loan or insurance applications.

July 24, 2025
LlamaIndex and Elasticsearch Rerankers: Unbeatable simplicity
Learn how to transition from Llamaindex RankGPT reranker to Elastic built-in semantic reranker.